Capabilities And Limitations Of Fsm Pdf
Border Gateway Protocol Wikipedia. Border Gateway Protocol BGP is a standardized exterior gateway protocol designed to exchange routing and reachability information among autonomous systems AS on the Internet. The protocol is often classified as a path vector protocol but is sometimes also classed as a distance vector routing protocolcitation needed. The Border Gateway Protocol makes routing decisions based on paths, network policies, or rule sets configured by a network administrator and is involved in making core routing decisions. BGP may be used for routing within an autonomous system. In this application it is referred to as Interior Border Gateway Protocol, Internal BGP, or i. BGP. In contrast, the Internet application of the protocol may be referred to as Exterior Border Gateway Protocol, External BGP, or e. BGP. Current versioneditThe current version of BGP is version 4 BGP4, which was published as RFC 4. RFC 1. 77. 1 version 4. RFC 4. 27. 1 corrected errors, clarified ambiguities and updated the specification with common industry practices. The major enhancement was the support for Classless Inter Domain Routing and use of route aggregation to decrease the size of routing tables. Copyright 2015 Juniper Networks, Inc. WHAT IS IN THE BGPFLOW SPEC NLRI A Flow Specification NLRI is defined which may include several. Welcome to the Teterboro Users Group TUG website, a single source for all of Teterboro Airports users to find helpful information pertaining to airport. Department of Homeland Security U. S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement. Complete Technical Acronyms, Glossary Definitions for PC, SAN, NAS, QA, Testing, HDTV, Wireless, Linux, Embedded, Networks, Video, Digital, pharma, Unix, Video. Capabilities And Limitations Of Fsm Pdf Converter' title='Capabilities And Limitations Of Fsm Pdf Converter' />Capabilities And Limitations Of Fsm Pdf Viewer

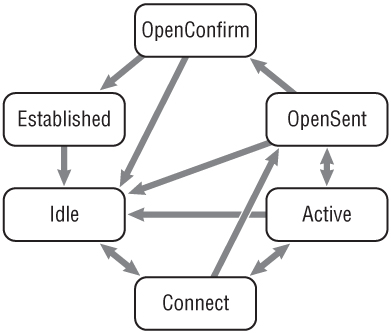 Issn 19849648 issn 21759146 online journal of aerospace technology and management vol. Gender and Educational Achievement Learning Objectives. To describe and analyse the main statistical relationships between gender and educational achievement. Capabilities And Limitations Of Fsm Pdf Compressor' title='Capabilities And Limitations Of Fsm Pdf Compressor' />BGP4 has been in use on the Internet since 1. BGP4 is standard for Internet routing, required of most Internet service providers ISPs to establish routing between one another. Very large private IP networks use BGP internally. An example is the joining of a number of large Open Shortest Path First OSPF networks, when OSPF by itself does not scale to the size required. Another reason to use BGP is multihoming a network for better redundancy, either to multiple access points of a single ISP or to multiple ISPs. OperationeditBGP neighbors, called peers, are established by manual configuration between routers to create a TCP session on port 1. A BGP speaker sends 1. Among routing protocols, BGP is unique in using TCP as its transport protocol. When BGP runs between two peers in the same autonomous system AS, it is referred to as Internal BGP i. BGP or Interior Border Gateway Protocol. When it runs between different autonomous systems, it is called External BGP e. BGP or Exterior Border Gateway Protocol. Routers on the boundary of one AS exchanging information with another AS are called border or edge routers or simply e. BGP peers and are typically connected directly, while i. BGP peers can be interconnected through other intermediate routers. Other deployment topologies are also possible, such as running e. BGP peering inside a VPN tunnel, allowing two remote sites to exchange routing information in a secure and isolated manner. The main difference between i. BGP and e. BGP peering is in the way routes that were received from one peer are propagated to other peers. For instance, new routes learned from an e. BGP peer are typically redistributed to all i. BGP peers as well as all other e. BGP peers if transit mode is enabled on the router. However, if new routes are learned on an i. BGP peering, then they are re advertised only to all e. BGP peers. These route propagation rules effectively require that all i. BGP peers inside an AS are interconnected in a full mesh. How routes are propagated can be controlled in detail via the route maps mechanism. This mechanism consists of a set of rules. Each rule describes, for routes matching some given criteria, what action should be taken. The action could be to drop the route, or it could be to modify some attributes of the route before inserting it in the routing table. Extensions negotiationeditDuring the peering handshake, when OPEN messages are exchanged, BGP speakers can negotiate6 optional capabilities of the session, including multiprotocol extensions and various recovery modes. If the multiprotocol extensions to BGP7 are negotiated at the time of creation, the BGP speaker can prefix the Network Layer Reachability Information NLRI it advertises with an address family prefix. These families include the IPv. IPv. 6, IPv. 4IPv. Virtual Private Networks and multicast BGP. Increasingly, BGP is used as a generalized signaling protocol to carry information about routes that may not be part of the global Internet, such as VPNs. Finite state machineseditIn order to make decisions in its operations with peers, a BGP peer uses a simple finite state machine FSM that consists of six states Idle Connect Active Open. Sent Open. Confirm and Established. For each peer to peer session, a BGP implementation maintains a state variable that tracks which of these six states the session is in. Aadhaar Card By Aadhaar No'>Aadhaar Card By Aadhaar No. The BGP defines the messages that each peer should exchange in order to change the session from one state to another. The first state is the Idle state. Free Download Sony Sound Forge 7 Portable Toshiba'>Free Download Sony Sound Forge 7 Portable Toshiba. In the Idle state, BGP initializes all resources, refuses all inbound BGP connection attempts and initiates a TCP connection to the peer. The second state is Connect. In the Connect state, the router waits for the TCP connection to complete and transitions to the Open. Sent state if successful. If unsuccessful, it starts the Connect. Retry timer and transitions to the Active state upon expiration. In the Active state, the router resets the Connect. Retry timer to zero and returns to the Connect state. In the Open. Sent state, the router sends an Open message and waits for one in return in order to transition to the Open. Confirm state. Keepalive messages are exchanged and, upon successful receipt, the router is placed into the Established state. In the Established state, the router can sendreceive Keepalive Update and Notification messages tofrom its peer. Idle State. Refuse all incoming BGP connections. Start the initialization of event triggers. Initiates a TCP connection with its configured BGP peer. Listens for a TCP connection from its peer. Changes its state to Connect. If an error occurs at any state of the FSM process, the BGP session is terminated immediately and returned to the Idle state. Some of the reasons why a router does not progress from the Idle state are. TCP port 1. 79 is not open. A random TCP port over 1. Peer address configured incorrectly on either router. AS number configured incorrectly on either router. Connect State. Waits for successful TCP negotiation with peer. Muscle Growth Flash Game there. BGP does not spend much time in this state if the TCP session has been successfully established. Sends Open message to peer and changes state to Open. Sent. If an error occurs, BGP moves to the Active state. Some reasons for the error are. TCP port 1. 79 is not open. A random TCP port over 1. Peer address configured incorrectly on either router. AS number configured incorrectly on either router. Active State. If the router was unable to establish a successful TCP session, then it ends up in the Active state. BGP FSM tries to restart another TCP session with the peer and, if successful, then it sends an Open message to the peer. If it is unsuccessful again, the FSM is reset to the Idle state. Repeated failures may result in a router cycling between the Idle and Active states. Some of the reasons for this include. TCP port 1. 79 is not open. A random TCP port over 1. BGP configuration error. Network congestion. Flapping network interface. Open. Sent State. BGP FSM listens for an Open message from its peer. Once the message has been received, the router checks the validity of the Open message. If there is an error it is because one of the fields in the Open message does not match between the peers, e.
Issn 19849648 issn 21759146 online journal of aerospace technology and management vol. Gender and Educational Achievement Learning Objectives. To describe and analyse the main statistical relationships between gender and educational achievement. Capabilities And Limitations Of Fsm Pdf Compressor' title='Capabilities And Limitations Of Fsm Pdf Compressor' />BGP4 has been in use on the Internet since 1. BGP4 is standard for Internet routing, required of most Internet service providers ISPs to establish routing between one another. Very large private IP networks use BGP internally. An example is the joining of a number of large Open Shortest Path First OSPF networks, when OSPF by itself does not scale to the size required. Another reason to use BGP is multihoming a network for better redundancy, either to multiple access points of a single ISP or to multiple ISPs. OperationeditBGP neighbors, called peers, are established by manual configuration between routers to create a TCP session on port 1. A BGP speaker sends 1. Among routing protocols, BGP is unique in using TCP as its transport protocol. When BGP runs between two peers in the same autonomous system AS, it is referred to as Internal BGP i. BGP or Interior Border Gateway Protocol. When it runs between different autonomous systems, it is called External BGP e. BGP or Exterior Border Gateway Protocol. Routers on the boundary of one AS exchanging information with another AS are called border or edge routers or simply e. BGP peers and are typically connected directly, while i. BGP peers can be interconnected through other intermediate routers. Other deployment topologies are also possible, such as running e. BGP peering inside a VPN tunnel, allowing two remote sites to exchange routing information in a secure and isolated manner. The main difference between i. BGP and e. BGP peering is in the way routes that were received from one peer are propagated to other peers. For instance, new routes learned from an e. BGP peer are typically redistributed to all i. BGP peers as well as all other e. BGP peers if transit mode is enabled on the router. However, if new routes are learned on an i. BGP peering, then they are re advertised only to all e. BGP peers. These route propagation rules effectively require that all i. BGP peers inside an AS are interconnected in a full mesh. How routes are propagated can be controlled in detail via the route maps mechanism. This mechanism consists of a set of rules. Each rule describes, for routes matching some given criteria, what action should be taken. The action could be to drop the route, or it could be to modify some attributes of the route before inserting it in the routing table. Extensions negotiationeditDuring the peering handshake, when OPEN messages are exchanged, BGP speakers can negotiate6 optional capabilities of the session, including multiprotocol extensions and various recovery modes. If the multiprotocol extensions to BGP7 are negotiated at the time of creation, the BGP speaker can prefix the Network Layer Reachability Information NLRI it advertises with an address family prefix. These families include the IPv. IPv. 6, IPv. 4IPv. Virtual Private Networks and multicast BGP. Increasingly, BGP is used as a generalized signaling protocol to carry information about routes that may not be part of the global Internet, such as VPNs. Finite state machineseditIn order to make decisions in its operations with peers, a BGP peer uses a simple finite state machine FSM that consists of six states Idle Connect Active Open. Sent Open. Confirm and Established. For each peer to peer session, a BGP implementation maintains a state variable that tracks which of these six states the session is in. Aadhaar Card By Aadhaar No'>Aadhaar Card By Aadhaar No. The BGP defines the messages that each peer should exchange in order to change the session from one state to another. The first state is the Idle state. Free Download Sony Sound Forge 7 Portable Toshiba'>Free Download Sony Sound Forge 7 Portable Toshiba. In the Idle state, BGP initializes all resources, refuses all inbound BGP connection attempts and initiates a TCP connection to the peer. The second state is Connect. In the Connect state, the router waits for the TCP connection to complete and transitions to the Open. Sent state if successful. If unsuccessful, it starts the Connect. Retry timer and transitions to the Active state upon expiration. In the Active state, the router resets the Connect. Retry timer to zero and returns to the Connect state. In the Open. Sent state, the router sends an Open message and waits for one in return in order to transition to the Open. Confirm state. Keepalive messages are exchanged and, upon successful receipt, the router is placed into the Established state. In the Established state, the router can sendreceive Keepalive Update and Notification messages tofrom its peer. Idle State. Refuse all incoming BGP connections. Start the initialization of event triggers. Initiates a TCP connection with its configured BGP peer. Listens for a TCP connection from its peer. Changes its state to Connect. If an error occurs at any state of the FSM process, the BGP session is terminated immediately and returned to the Idle state. Some of the reasons why a router does not progress from the Idle state are. TCP port 1. 79 is not open. A random TCP port over 1. Peer address configured incorrectly on either router. AS number configured incorrectly on either router. Connect State. Waits for successful TCP negotiation with peer. Muscle Growth Flash Game there. BGP does not spend much time in this state if the TCP session has been successfully established. Sends Open message to peer and changes state to Open. Sent. If an error occurs, BGP moves to the Active state. Some reasons for the error are. TCP port 1. 79 is not open. A random TCP port over 1. Peer address configured incorrectly on either router. AS number configured incorrectly on either router. Active State. If the router was unable to establish a successful TCP session, then it ends up in the Active state. BGP FSM tries to restart another TCP session with the peer and, if successful, then it sends an Open message to the peer. If it is unsuccessful again, the FSM is reset to the Idle state. Repeated failures may result in a router cycling between the Idle and Active states. Some of the reasons for this include. TCP port 1. 79 is not open. A random TCP port over 1. BGP configuration error. Network congestion. Flapping network interface. Open. Sent State. BGP FSM listens for an Open message from its peer. Once the message has been received, the router checks the validity of the Open message. If there is an error it is because one of the fields in the Open message does not match between the peers, e.